Post Electrophoretic Analysis Articles
The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
Electrophoresis System Dynamics
The apparatus in gel electrophoresis constitutes an electrical/thermodynamic system. The apparatus receives energy from the power source and releases energy as heat. The figure below shows a stylized representation of a typical vertical slab gel apparatus. The gel, perfused with buffer solution and held between two glass plates, has been clamped in position, its upper end is immersed in the buffer solution of the upper electrode chamber. The lower end of the gel is immersed in the lower electrode chamber, which contains buffer solution as well.
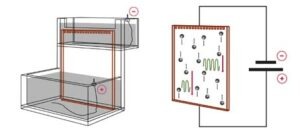
A gel electrophoresis apparatus is essentially a resistor (the gel) connected to a voltage source, creating a simple DC circuit. The voltage drop across the gel provides the motive force which drives the buffer and sample ions through the gel.
After samples are introduced into the sample wells at the top of the matrix, the electric field between the electrode chambers causes them to migrate toward the lower chamber. The electrophoresis apparatus can be viewed as a simple DC circuit composed of one voltage source and three resistors in series, the resistors being the upper chamber, the gel, and the lower chamber. Because the cross-section of each electrode chamber is much greater than the cross-section of the gel slab, and because the chambers are shorter in length as well, the vast majority of the resistance in the circuit derives from the gel slab. For this reason, it is sufficient to consider the gel slab as the only resistor in the circuit, where the vast majority of power is expended. An exception to this rule occurs if buffer salts are inadvertently absent from one or both of the electrode chambers.
NEXT TOPIC: The Electrophoresis Matrix
