DNase I Footprinting
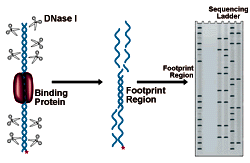
DNase I Footprinting Procedure
- Preparing the DNA substrate:
DNA to be analyzed must be cloned in such a way as to present a restriction site for an enzyme leaving a 5' overhang (3' recessed OH) 50-150 bp from the putative binding site. This site is labeled by "filling in" the recessed site with 32P-dNTPs using DNA polymerase. The probe is then cut from the remaining plasmid by a second restriction enzyme, 150 bases on the opposite side of the binding site. This releases a 200-300 bp probe, labeled at one end (see figure below).- Digest 5-10 picomoles of plasmid (10-20µg of a 3000bp construct) with an enzyme that will leave a recessed 3' end 50-150bp from the binding site.
- Ethanol precipitates the DNA, and wash 1X with 70% ethanol.
- Add 50 µl of 1X Klenow buffer containing 50 µCi of each 32P dNTP. Add 10 units of Klenow fragment (see below) in < 2 µl, and incubate 30 minutes at 25°C.Klenow buffer:
- 50mM Tris HCl, pH 7.6
- 12mM MgCl
- 1mM DTT
- 50 µg/ml BSA
- Chase reaction with 5 µl of 2mM each dCTP, dGTP, dTTP, dATP, to ensure complete polymerization.
- Ethanol precipitate twice with 0.1 vol 3M sodium acetate and 3 volumes of ethanol, or purify with a spin column or glass powder elution to remove the unincorporated label.
- Cut with a restriction enzyme to release a 200-300 bp end-labeled probe.
- Run probe on a 1.5-2% agarose gel and recover fragment by electroelution. Further purification may be necessary to ensure consistent results. Ion exchange mini-columns provide good results.
- If the volume is less than 50µl, ethanol precipitate the probe, and reconstitutes in 50 µl TE buffer.
- Bind Protein to DNA Probe:
- Mix 105 cpm of the probe with 200 µl of DNase footprinting buffer (see below for formulation) DNase Footprinting Buffer:
- 10mM Tris HCl, pH 7.6
- 4mM MgCl2
- 1mM CaCl2
- 150mM KCl
- 2mM DTT
- 100 µg/ml BSA
- 2mg/ml calf thymus DNA pH 7.6 (adjust buffer if necessary)
- Add 20 µl protein sample. A series of dilutions covering 4-5 orders of magnitude will allow calculation of the binding affinity.
- Prepare a blank tube with 20 µl of assay buffer.
- Incubate 30-45 minutes, at equilibration temperature. The optimum time and temperature must be determined for each DNA/probe combination.
- Mix 105 cpm of the probe with 200 µl of DNase footprinting buffer (see below for formulation) DNase Footprinting Buffer:
- DNase I Treatment:
DNase treatment proceeds for only 2 minutes, so stop solution and a dry ice ethanol bath must be prepared before beginning the treatment. The stop solution formulation is as follows:- 6.5 ml ethanol
- 50 µl 1mg/ml tRNA
- 0.5 ml ammonium acetate saturated solution
Procedure:
- Cool the aforementioned stop solution to -70°C prior to use.
- Prepare DNase I solution. The amount of DNase I required will vary depending upon the purity, age, and storage conditions used for the enzyme. Start with 0.1 mg/ml DNase I and adjust to get an average of 1 nick per DNA molecule.
- Dissolve DNase I in assay/equilibration buffer without BSA or calf thymus DNA.
- Add 5 µl DNase I solution for each 200 µl sample of protein/DNA.
- A pipette is as necessary. Reproducible pipetting is essential at this stage if different DNAµprotein ratios are to be compared.
- Incubate at equilibration temperature for exactly 2 minutes, then add 800 µl stop solution at -70°C.
- Precipitate DNA at -70°C for 30 minutes. Wash pellet with 70% ethanol twice, and remove all supernatant. Air dry or speed vac 10 minutes.
- Redissolve pellet in 6 µl of loading buffer, and run on a standard denaturing PAGE gel.
Interpreting the results of DNase Footprinting
The figure below shows an electrophoresis gel of idealized results. Bands correspond to DNase I cleavage sites. As the amount of protein present increases, the footprint area is progressively protected from cleavage. The concentration of protein required to give 50% protection can be mathematically related to the equilibrium constant for protein binding. See CPMB Section 12.4 for a complete discussion of this method of analysis.
NEXT TOPIC: Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
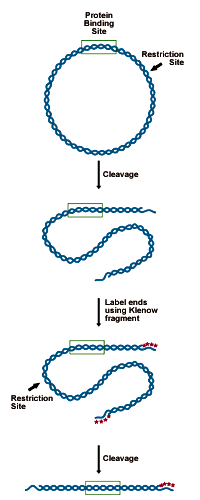
Preparing the DNA substrate for DNase footprinting analysis. A circular construct containing the protein binding site is linearized with a restriction endonuclease, yielding two free ends, which are both labeled. One end is then cut away in a second round of restriction digestion, leaving an end-labeled probe which carries the binding site.
