Electrophoresis
Glass Bond
$108.00
- Chemically bonds the gel to the glass plate
- Prevents cracking and tearing of the gel
Description
- Chemically bonds the gel to the glass plate
- Prevents cracking and tearing of the gel
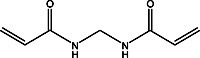
National Diagnostics’ Glass Bond allows polyacrylamide gels to be affixed to one of the glass plates used for casting electrophoresis gels. The glass plate is chemically modified so the gel becomes covalently bound to the glass, enabling it to be manipulated without danger of the gel ripping or slipping off the plate. Glass Bond is especially convenient for treating large sequencing plates, as subsequent manipulation can be performed without fear of ripping or disrupting the gel. On plates treated with Glass Bond, the gels dry down to a smooth plastic film without using a gel dryer, allowing autoradiography to be performed more easily. A total of 6.25 liters of bonding solution (enough for over 100 applications on 40 X 40 cm glass plates) can be made from one 25 ml bottle of Glass Bond.
Storage: Glass Bond is best stored tightly capped in a cool dry area.
Additional information
| Weight | .3 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 6 × 3 × 3 in |
Protocol
Glass Bond Method of Uses
WARNING: Always work with Glass Bond in a hood.
- Ensure plates are clean and dry before starting the bonding procedure. If not clean, soak in 20% sodium hydroxide.
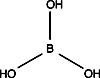
- Prepared enough bonding solution to fully submerge all the plates to be treated. Adjust the pH of 500 mL water by adding about 50µl glacial acetic acid. Add 20 mL Glass Bond and mixe well with magnetic stirrer until liquid dissolves.
- Pour Glass Bond solution into vessel containing the clean plates. Move plates to release trapped air bubbles. Incubate for 1-3 hours.
- Remove plates from vessel and rinse with distilled water. Allow plates to air dry then wipe clean
- Store plates interleaved between sheets of dry paper in plastic storage bag. Note: Acrylamide gels denatured with urea will crack upon drying unless fixed in 10% acetic acid/10% methanol solution for 30 minutes.
- If gels must be removed intact from the plate submerge the plate with the gel in water and carefully run a razor between them. For gels dried on the glass surface, rehydrate the gel by soaking in distilled water for 2-3 hours before attempting to detach.
Safety Overview
Safety Summary (see SDS for complete information before using product):
Appearance and Odor:
Clear colorless solution with acrid odor.
Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of water.
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
IRRITATING TO EYES, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM, AND SKIN. AVOID HEAT, FLAMES AND SPARKS.
- UV Shadowing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- Uneven Staining
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix-Buffer Strength
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Ohm’s Law
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
- The Electrophoresis Matrix
- The Agarose Matrix
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- SSCP Analysis
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
- Sample Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- PFGE and FIGE
- Peptide Mapping
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Multiphasic Buffer Systems
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Measuring Molecular Weight with SDS-PAGE
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- Isotachophoresis
- Isoelectric Focusing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Immuno-Electrophoresis / Immuno-Diffusion
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – Vertical Tube Gels
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Vertical Slab Gel System
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Horizontal Gel System
- Homogeneous Buffer Systems
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Guide Strip Technique
- Gel Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of RNA & Post Electrophoretic Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Electrophoresis Buffers-Choosing the Right Buffer
- Electrophoresis Buffers–The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Conformational Analysis
- Casting Gradient Gels
- Buffer Additives-Surfactants
- Buffer Additives-Reducing Agents
- Buffer Additives-Hydrogen Bonding Agents
- Blotches on Gel
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
- Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
- Activity Stains