Post Electrophoretic Analysis
Guide Strip Technique
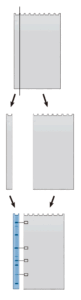
In the Guide Strip Technique, a parallel lane is excised and stained to guide band excision.
In certain instances, the effects of staining a protein may interfere with subsequent analysis. Examples are Coomassie staining when enzymatic activity is required, or silver staining prior to amino acid analysis when covalent modification of the amino acids will give spurious results. In these cases, it is common to use a “guide strip”. A guide strip is a lane that is run parallel to the lane to be analyzed and contains either size markers or a duplicate sample. After the gel is run, the guide strip is cut off and stained, and then realigned with the gel and used as a template to guide band excision. The technique is straightforward. The only common error is to fail to re-equilibrate the gel with running buffer after staining. As many stains cause shrinkage or swelling of the gel, re-equilibration is necessary for accurate and consistent realignment.
NEXT TOPIC: Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- UV Shadowing
- Uneven Staining
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Guide Strip Technique
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Blotches on Gel
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
