Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
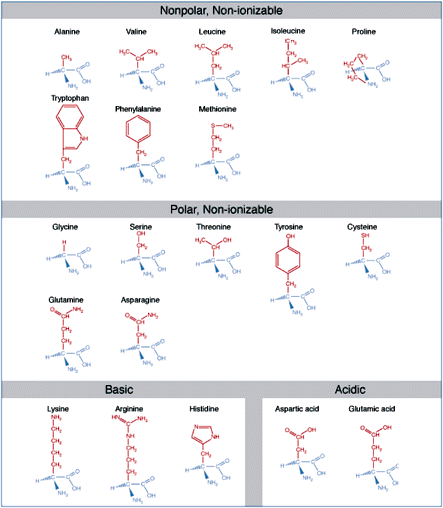
Proteins Like nucleic acids, proteins are polymers. While with nucleic acids the repeating unit is the nucleotide, with proteins, the analogous repeating unit is the amino acid. Amino acids consist of a central carbon that carries an amino group, a carboxyl group, hydrogen, and a side-chain group. Amino acids are distinguished by the properties of…
Read MoreBiological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
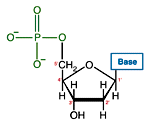
Nucleic Acids Like many biological molecules nucleic acids are polymers, long molecules formed of repeating units. With nucleic acids, the repeating unit is the nucleotide. A nucleotide consists of a five carbon sugar, a nitrogen containing base and a phosphate group. The two primary kinds of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA),…
Read MoreMechanism of Liquid Scintillation Counting
By eliminating the combustion steps needed for gas phase analysis, the introduction of liquid scintillation counting (LSC) reduced the time required to analyze radioactive samples from hours to minutes. For low energy (“soft”) β emitters, LSC offers unmatched convenience and sensitivity. LSC detects radioactivity via the same type of light emission events which are used…
Read MoreDenaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
In their native form, proteins fold into a variety of shapes, some compact, some elongated. The rate of migration of native proteins through a sieving medium is therefore more a reflection of their relative compactness, and less an accurate measure of molecular weight. Denaturing the proteins nullifies structural effects on mobility, allowing separation on a…
Read More