Biological Macromolecules
Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
Radioactive decay occurs with the emission of particles or electromagnetic radiation from an atom due to a change within its nucleus. Forms of radioactive emission include alpha particles (α), beta particles (β), and gamma rays (γ). α particles are the least energetic, most massive of these decay products. An α particle contains two protons and…
Read MoreBiological Macromolecules – Proteins
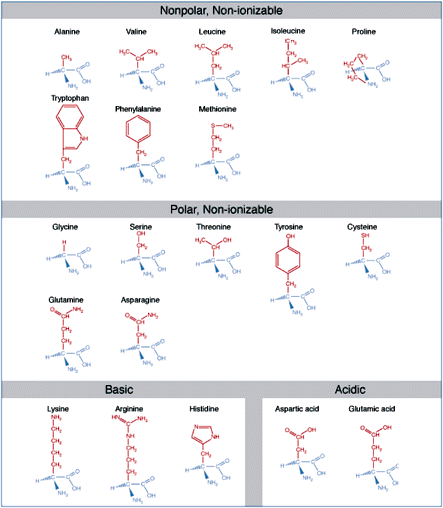
Proteins Like nucleic acids, proteins are polymers. While with nucleic acids the repeating unit is the nucleotide, with proteins, the analogous repeating unit is the amino acid. Amino acids consist of a central carbon that carries an amino group, a carboxyl group, hydrogen, and a side-chain group. Amino acids are distinguished by the properties of…
Read MoreBiological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
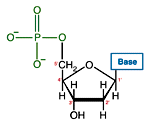
Nucleic Acids Like many biological molecules nucleic acids are polymers, long molecules formed of repeating units. With nucleic acids, the repeating unit is the nucleotide. A nucleotide consists of a five carbon sugar, a nitrogen containing base and a phosphate group. The two primary kinds of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA),…
Read More