Fundamental Principles of Electrophoresis
The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
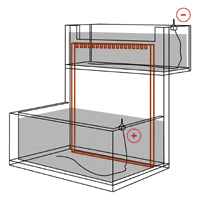
Electrophoresis System Dynamics The apparatus in gel electrophoresis constitutes an electrical/thermodynamic system. The apparatus receives energy from the power source and releases energy as heat. The figure below shows a stylized representation of a typical vertical slab gel apparatus. The gel, perfused with buffer solution and held between two glass plates, has been clamped in…
Read MoreThe Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
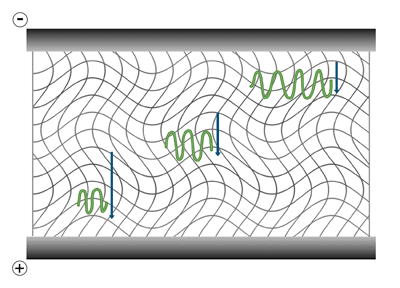
The term “electrophoresis” refers simply to the movement of particles by an electric force. The first electrophoresis experiments were carried out on molecules in a conductive buffer solution, where the only force acting on the sample was the electric field. The vast majority of current laboratory techniques are performed in a matrix perfused by an…
Read MoreBiological Macromolecules – Proteins
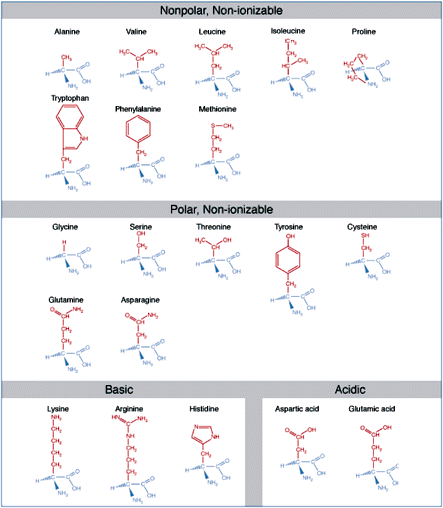
Proteins Like nucleic acids, proteins are polymers. While with nucleic acids the repeating unit is the nucleotide, with proteins, the analogous repeating unit is the amino acid. Amino acids consist of a central carbon that carries an amino group, a carboxyl group, hydrogen, and a side-chain group. Amino acids are distinguished by the properties of…
Read MoreBiological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
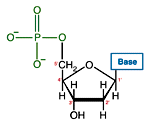
Nucleic Acids Like many biological molecules nucleic acids are polymers, long molecules formed of repeating units. With nucleic acids, the repeating unit is the nucleotide. A nucleotide consists of a five carbon sugar, a nitrogen containing base and a phosphate group. The two primary kinds of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA),…
Read More