Electrophoresis
Autofluor
$299.00
Quantity discount when you buy four or more bottles!Catalog Number: LS-315Size: 1 liter
- High-resolution autoradiographic image intensifier
- Rapid enhancement of low energy beta-emitters
- For polyacrylamide gels, paper chromatography, and TLC plates
- Water-based, odorless, contains no DMSO
Description
Catalog Number: LS-315
Size: 1 liter
- High-resolution autoradiographic image intensifier
- Rapid enhancement of low energy beta-emitters
- For polyacrylamide gels, paper chromatography, and TLC plates
- Water-based, odorless, contains no DMSO
-
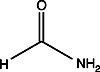
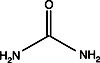
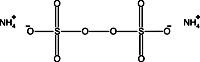
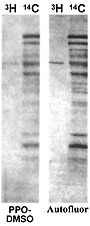
In the figure to the left, the gel on the left (7%, 1mm) was dehydrated in DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide) for one hour, then impregnated in PPO-DMSO for one hour and precipitated and dried. The gel on the right was impregnated with Autofluor for one hour and dried. Both gels were exposed for 24 hours at -76°C on Kodak XR-5 X-OMat film. The single tritiated band contains 5000 dpm. Note the higher degree of resolution and band discrimination with Autofluor vs PPO-DMSO.The Autofluor procedure is the shortest and easiest procedure yet developed for enhancement and visualization of beta-emitters. In an independent test comparing eight different fluorographic methods for the detection of 35S-labeled proteins in polyacrylamide gels, Autofluor was the most effective. With Autofluor, the dpm/mm2 required to half-saturate the x-ray film was 1/8 that required by autoradiography alone.
Storage: Autofluor has a shelf life of at least one year stored at room temperature, out of direct sunlight. Keep from freezing. At temperatures less than 20°C precipitation of water soluble phosphors may occur. Warming to approximately 30°C will redissolve the phosphors.
Additional information
| Weight | 4.8 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 7 × 7 × 14 in |
Protocol
After staining, fix the gel with 5% glacial acetic acid, 5% isopropyl alcohol, and 90% water. Fix for 15 to 20 minutes. Pour off fixing solution and discard according to radioactive disposal procedures.
2. Rinse the gel in a continuous flow of tap water for 15 minutes to assure the complete removal of acetic acid residue.
[To prevent crystal formation, it is important that the gel be thoroughly rinsed after fixing. Should the gel develop white crystals on contact with Autofluor, dissolve the precipitate by soaking the gel in a solution of 1g sodium carbonate/100ml water or 1X TRIS Buffer. Soak the gel in Autofluor until the white precipitate dissolves. Repeat from the beginning of step two.}
3. Cover gel with Autofluor until the depth of Autofluor is twice the thickness of the gel. Gently agitate in Autofluor for 30 min/mm of gel thickness. Pour off remaining Autofluor and retain for future use. Label reserved material as radioactive. Autofluor may be reused several times before a diminishing response is observed.
4. DO NOT WASH GEL. Place directly on filter paper and dry on gel dryer under heat (80°C) and vacuum.
5. The gel will have a white to light tan sparkling appearance similar to freshly fallen snow.
6. Place on film and expose at -76°C. Due to the higher light output of the Autofluor phosphor, less exposure time is needed for gels treated with Autofluor than for gels treated with PPO/DMSO. Sufficient exposure time for a 5000 dpm/band is 24 hours. Overexposure of the film will cause the bands to become fuzzy and resolution to be lost.
7. Develop film according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- UV Shadowing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- Uneven Staining
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix-Buffer Strength
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Ohm’s Law
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
- The Electrophoresis Matrix
- The Agarose Matrix
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- SSCP Analysis
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
- Sample Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- PFGE and FIGE
- Peptide Mapping
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Multiphasic Buffer Systems
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Measuring Molecular Weight with SDS-PAGE
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- Isotachophoresis
- Isoelectric Focusing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Immuno-Electrophoresis / Immuno-Diffusion
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – Vertical Tube Gels
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Vertical Slab Gel System
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Horizontal Gel System
- Homogeneous Buffer Systems
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Guide Strip Technique
- Gel Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of RNA & Post Electrophoretic Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Electrophoresis Buffers-Choosing the Right Buffer
- Electrophoresis Buffers–The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Conformational Analysis
- Casting Gradient Gels
- Buffer Additives-Surfactants
- Buffer Additives-Reducing Agents
- Buffer Additives-Hydrogen Bonding Agents
- Blotches on Gel
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
- Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
- Activity Stains