Electrophoresis
ProtoBlue Safe
Price range: $75.00 through $323.00
Get a free sample of ProtoBlue Safe! Call us at (800) 526-3867 for details!
- Fast, Easy to Use Protocol
- Ecofriendly; Nonhazardous disposal
- Costs Less than Regular Coomassie
Description
Get a free sample of ProtoBlue Safe! Call us at (800) 526-3867 for details!
- Fast, Easy to Use Protocol
- Ecofriendly; Nonhazardous disposal
- Costs Less than Regular Coomassie
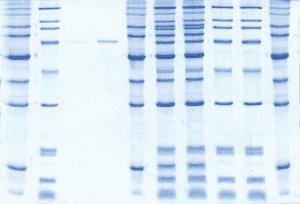
The Best Performing Colloidal Stain – Detects as little as 5ng protein
Compared to similar stains, the more finely controlled colloidal structure of ProtoBlue Safe improves both the sensitivity and the universality of staining. ProtoBlue Safe is less prone to high background caused by trace residual SDS in the gel.
Costs Less than Regular Coomassie
Laboratories typically spend twice as much per gel in the methanol and acetic acid for staining and destaining with regular Coomassie than for ProtoBlue Safe (including ethanol cost). In addition, ProtoBlue Safe is much faster, more sensitive, and you can pour the used stain solution down the drain. Protein visualization is faster, safer, more sensitive and less expensive with ProtoBlue Safe.
Nonhazardous Disposal
Used stain solution is not a hazardous waste (as defined by United States Title 40 Code of Federal Regulations (40 CFR 261.24(a)).
Fast Protocol – No Methanol or Acetic Acid
Your sample can be detected with these three quick, easy steps:
- Wash gel three times for five minutes with deionized water on an orbital shaker.
(Note: This step is optional. A longer incubation in stain solution and longer post-stain washing can substitute for this wash step.) - Add one part ethanol to nine parts staining solution while stirring. Adding ethanol greatly improves sensitivity, reproductivity and shelf life compared to solutions that add ethanol at point of manufacture.
- Add enough staining solution to completely cover the gel. Bands containing more than 1 μg will be detected within 15 minutes.
(Note: For sensitivity up to 5 ng, incubate the gel in stain for at least five hours.)
Additional information
| Weight | 0.1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 8 × 8 × 16 in |
Protocol
Prepare Working Solution
- Gently invert the bottle several times to resuspend colloidal dye particles that settle out on standing.
- Add 1 part ethanol to 9 parts staining solution while stirring. (Standard denatured ethanol is fine). A 20ml to 50ml volume of working solution is typically prepared, depending on the shape and size of the staining container. To preserve solution, we recommend a plastic staining container just big enough to hold the gel.
Procedures for Gel Staining
- Prepare ProtoBlue Safe Working Solution (above).
- Wash the gel 3 times with 5 minutes each with deionized water on an orbital shaker. Decant wash solution.
- After the last wash, add enough ProtoBlue Safe Working Solution to completely cover the gel.
- Bands containing more than 1μg of protein will be detected within 15 minutes. For full sensitivity incubate the gel in the stain for at least 4-5 hours. Longer incubations in the stain will not adversely affect the gel or the staining sensitivity.
- Remove the stain and wash the gel in deionized water. Incubating the gel in water increases the sensitivity of detection by reducing the background to crystal clear. The gel is stable in water for up to a week without loss of sensitivity. There is no need to store the gel in a salt solution.
Safety Overview
Safety Summary (see SDS for complete information before using product):
Appearance and Odor
Blue solution.
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
MAY CAUSE IRRITATION TO SKIN AND EYES. DUST LEFT AFTER SOLVENT EVAPORATION MAY CAUSE IRRITATION TO THE RESPIRATORY TRACT.