Post Electrophoretic Analysis Articles
Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
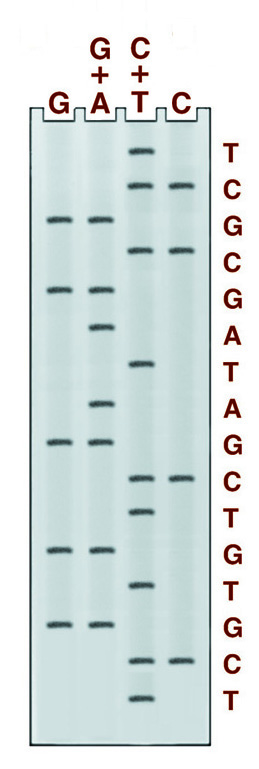
There are four chemical cleavage reactions at the core of the Maxam and Gilbert sequencing system. The figure below left shows an example from these reactions, the reaction cleaving specifically at guanine. The other three reactions cleave at G+A, C+T, or C. Guanine and cytosine, therefore, give bands in 2 lanes, adenine, and thymine in only one. An example of the gel pattern produced is presented below right.
Maxam and Gilbert DNA sequencing reaction specific for guanidine residues. The Guanine base is first modified with dimethyl sulfate (DMS), which makes the chain susceptible to cleavage by piperidine, destroying the guanidine residue and releasing a labeled fragment for electrophoresis.
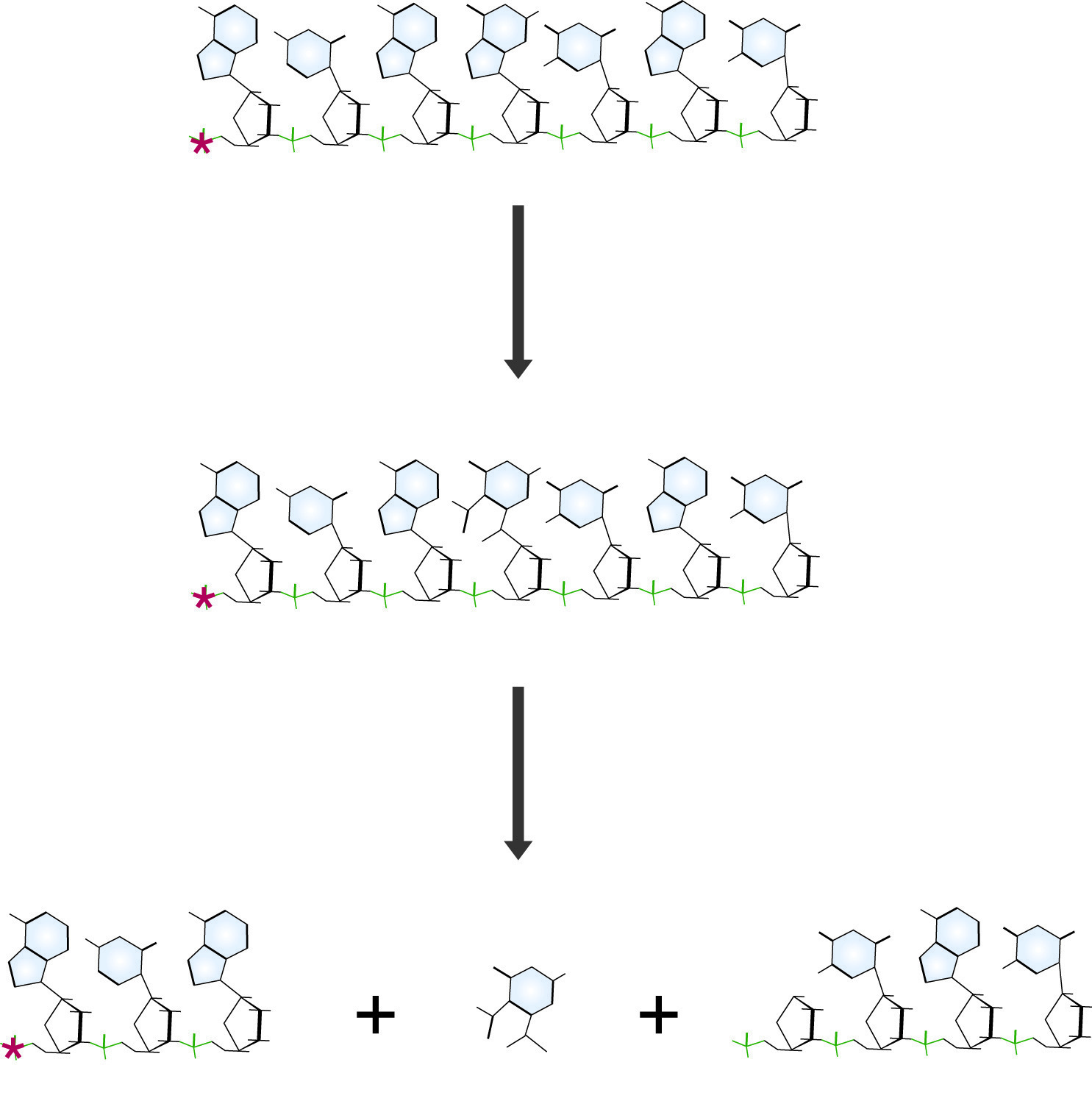
Maxam and Gilbert DNA sequencing reaction specific for guanidine residues. The Guanine base is first modified with dimethyl sulfate (DMS), which makes the chain susceptible to cleavage by piperidine, destroying the guanidine residue and releasing a labeled fragment for electrophoresis.
The DNA to be sequenced must first be end-labeled, at one end only. This is accomplished by kinase treatment with 32P ATP, which labels both ends, followed by restriction digestion and isolation of the two labeled fragments. Alternatively, the digestion of a plasmid containing a clone of the DNA of interest with an appropriate enzyme can yield a unique labeling site. Plasmid vectors containing the rare site for Tth111I, which leaves a single 5' base overlap, have been generated for this purpose. Cleavage with Tth111I leaves a G at one end and a C at the other in these vectors. By filling in the gap with the Klenow polymerase fragment in the presence of dGTP or dCTP, one end or the other can be labeled specifically. Labeled DNA is first precipitated to remove any salts which might interfere with the cleavage reactions. It is then modified, cleaved, and run on a denaturing gel for analysis. NB: THE HYDRAZINE AND DMS USED IN THESE PROTOCOLS ARE TOXIC AND VOLATILE. KEEP TUBES SEALED AND WORK IN A HOOD.
Maxam and Gilbert Sequencing Reactions
- Precipitate the substrate: To the 32P labeled DNA, add 0.1 vol. 3M Sodium Acetate and 1 vol. Isopropanol. Precipitate at -70°C for 10 minutes, and centrifuge at max RPM in a microcentrifuge for 5 minutes to collect the DNA. Wash the pellet twice with 1 ml cold 70% ethanol to remove all salt. Redissolve the DNA in 45 µl of sterile water. Count one microliter of the solution in the scintillation cocktail to confirm >5x103 >cpm total counts.
- Aliquot 10 µl of the DNA solution into each of the 4 tubes. Label the tubes C, G, C+T, G+A.
- Reactions:
- C: Add 10µl 2.5M NaCl and mix well. Add 30µl of Hydrazine (toxic!) and incubate at 25°C for 7-9 minutes.
- G: Add 200µl of: 50mM sodium cacodylate, pH 8, 1mM EDTA. Mix well and add 1µl Dimethyl Sulfate (DMS) (Toxic!) and incubate at 25°C for 4-5 minutes.
- C+T: Add 10µl H2O and mix well. Add 30µl Hydrazine and incubate at 25°C for 7-9 minutes.
- G+A: Add 25µl of formic acid, mix well and incubate at 25°C for 4-5 minutes.
- Stop the reactions:
Stop buffers:- G reaction: Add 50µl of:1.5M sodium acetate pH 7, 1M mercaptoethanol, 100µg/ml tRNA.
- All other reactions: Add 200µl of 0.3M sodium acetate, pH 7, 0.1mM EDTA, 25µg/ml tRNA.
Ethanol precipitation: Add 750µl of Ethanol, and transfer reactions to a -70°C bath for 5 minutes. Collect DNA by microcentrifugation for 5 minutes. Discard the supernatants as appropriate for DMS or Hydrazine waste. Rinse the pellets twice with 70% ethanol. Redissolve the pellets in 300µl of water, and add 30µl of 3M sodium acetate and 1ml of ethanol. Pellet DNA and wash twice with 70% ethanol. Allow the pellets to air dry.
- Piperidine cleavage reactions:
Resuspend pellets in 75µl of 10% piperidine, and transfer to screw-top tubes. It is essential that the tubes used for the piperidine reaction seal well in order to ensure that the reaction goes to completion. Incubate the tubes at 90°C for 30 minutes. Cool the tubes, centrifuge briefly to collect the condensate, and evaporate to dryness in a speed vac. Redissolve the pellet in 40µl of water and dry again. Repeat the rehydration and drying once more to ensure that all of the piperidines has been removed. The samples are now ready for denaturing PAGE.
NEXT TOPIC: Sanger Sequencing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- SSCP Analysis
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- PFGE and FIGE
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Conformational Analysis
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
