Post Electrophoretic Analysis
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
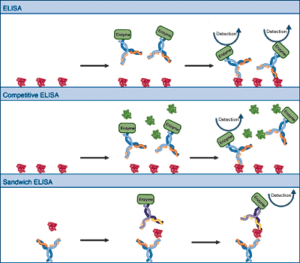
The variations of ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay). Top: Basic ELISA, in which antigen is bound to a surface and probed with enzyme linked antibody, providing semi-quantitative information. Middle: Competitive ELISA. Purified antigen is bound to the surface. Probing is carried out in the presence of samples or dilutions of free antigen (standards). The free antigen competes with the bound antigen, reducing the amount of antibody bound. Comparison between samples and standards yields quantitative information. Bottom: Sandwich ELISA, using one antibody to capture the antigen and another to detect it, resulting in increased specificity.
One of the most straightforward applications of immunological detection is the ELISA or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In the simplest system, the bound antigen is probed with antibodies that carry covalently attached enzyme molecules. Antibody binding immobilizes the enzyme in the vicinity of the bound antigen, allowing detection of the antigen. Variations include a competition ELISA in which a sample antigen is used to titrate the antibody from the bound antigen. In this system, the comparison of signals with signals from known antigen standards allows very accurate quantitation. In sandwich (capture) ELISAs, the antibody is bound to a surface and used to capture the antigen for detection by a second antibody. Sandwich ELISAs are extremely specific because the antigen must react with 2 antibodies to be detected. ELISA signals may be chromogenic and interpreted by the eye or spectrophotometer, or luminogenic and detected by a luminometer. Typically, ELISA's are run in 96 well plates which are scanned (and sometimes processed) by automated devices.
NEXT TOPIC: Overview of Western Blotting
- UV Shadowing
- Uneven Staining
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Guide Strip Technique
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Blotches on Gel
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
