Electrophoresis
ProtoGel Quick-Cast 12%
$46.00 – $150.00
- Ideal for Western Blotting Applications
- Cast a 12% Gel in One Fourth the Time
- Eliminates Mixing and Measuring
- Precast Convenience without the Precast Price
Description
- Ideal for Western Blotting Applications
- Cast a 12% Gel in One Fourth the Time
- Eliminates Mixing and Measuring
- Precast Convenience without the Precast Price
For even sharper bands and higher resolution, try Protogel Quick-Cast Loading Buffer. Specially formulated to give superior results on Quick Cast Gels. Now your Quick-Cast gels give even better results!
Ideal for Western Blotting
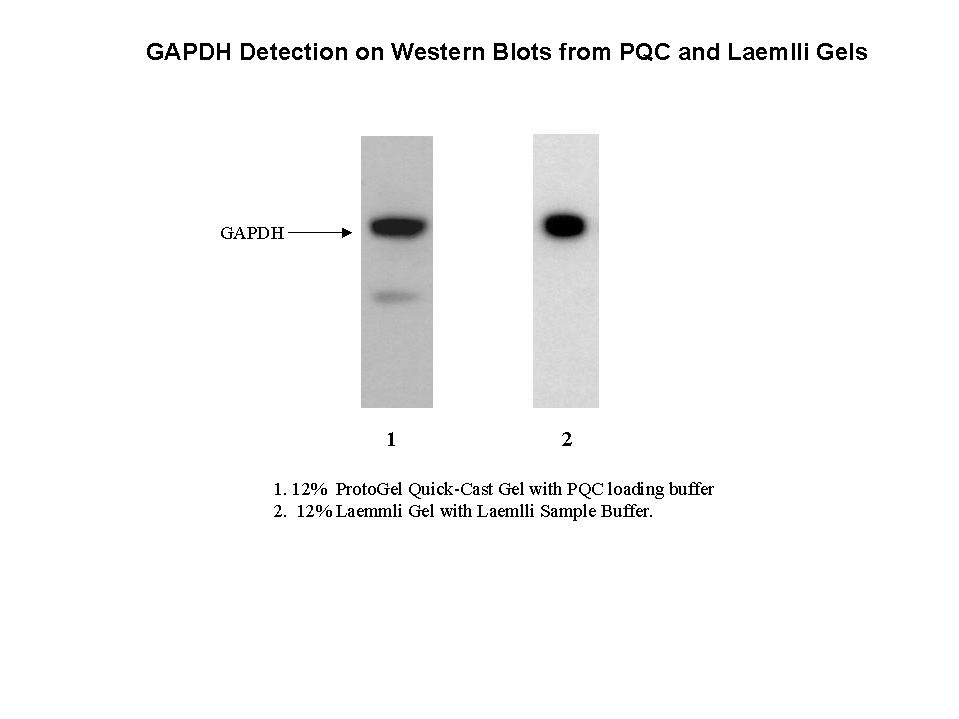
Mouse liver protein (25mg) was resolved on either a 12% Protogel Quick Cast gel (1) or a 12% Laemlli gel (2) and blotted to PVDF. The respective blots were probed an Anti-GAPDH antibody @ 1:50,000 dilution and an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody @ 1:50,000 dilution. The blots were detected with ProtoGlow ECL substrate.
Additional information
| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 7 × 7 × 11 in |
Protocol
Twenty Minute Casting
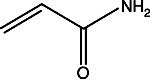
ProtoGel Quick-Cast contains the monomers and buffer components to produce a 12% gel.
- Measure out the volume of ProtoGel Quick-Cast needed to fill the cassette – typically 10ml for one mini-gel, 15ml for two.
- Add 100 microliters of fresh 10% APS and 10 microliters of TEMED per 10ml ProtoGel Quick-Cast. Mix briefly and pour into the gel cassette.
- 3. Insert comb and allow to polymerize at room temperature for 20 minutes. The gel is now ready to run.
For best results, it is recommended you use ProtoGel Quick-Cast Loading Buffer. Simply mix your samples with an equal volume of ProtoGel Quick-Cast Loading Buffer, load and run.
Safety Overview
Safety Summary (see SDS for complete information before using product):
Appearance and Odor:
Clear, colorless odorless solution.
Neurotoxin. May cause cancer. May cause heritable genetic damage. Also toxic in contact with skin and if swallowed. Danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation, in contact with skin or if swallowed.
Avoid exposure, obtain special instructions before use. In case of accident or if you feel ill, seek medical advice immediately (show the label where possible).
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
WARNING! ACRYLAMIDE IS A NEUROTOXIN. HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED. MAY CAUSE ALLERGIC SKIN REACTION. MAY CAUSE EYE IRRITATION. POLYMERIZATION MAY OCCUR FROM EXCESSIVE HEAT OR CONTAMINATION.
- UV Shadowing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- Uneven Staining
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix-Buffer Strength
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Ohm’s Law
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
- The Electrophoresis Matrix
- The Agarose Matrix
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- SSCP Analysis
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
- Sample Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- PFGE and FIGE
- Peptide Mapping
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Multiphasic Buffer Systems
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Measuring Molecular Weight with SDS-PAGE
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- Isotachophoresis
- Isoelectric Focusing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Immuno-Electrophoresis / Immuno-Diffusion
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – Vertical Tube Gels
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Vertical Slab Gel System
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Horizontal Gel System
- Homogeneous Buffer Systems
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Guide Strip Technique
- Gel Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of RNA & Post Electrophoretic Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Electrophoresis Buffers-Choosing the Right Buffer
- Electrophoresis Buffers–The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Conformational Analysis
- Casting Gradient Gels
- Buffer Additives-Surfactants
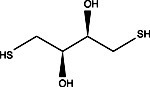
- Buffer Additives-Reducing Agents
- Buffer Additives-Hydrogen Bonding Agents
- Blotches on Gel
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
- Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
- Activity Stains