Electrophoresis
ND Protein Precipitation Kit
$147.00
Catalog number: EC-888
Size: 1 Kit
- Recovery of All Proteins from Complex Mixtures
- Precipitates as Little as 100ng of BSA at 0.25µg/ml
- Milder than TCA
- More Reliable than Acetonitrile or Ammonium Sulfate
Description
Catalog number: EC-888
Size: 1 Kit
- Recovery of All Proteins from Complex Mixtures
- Precipitates as Little as 100ng of BSA at 0.25µg/ml
- Milder than TCA
- More Reliable than Acetonitrile or Ammonium Sulfate
The ND Protein Precipitation Kit is mild on samples and easy to use. It casts the finest net of any procedure, allowing the high yield collection of all proteins in solution, precipitating even the most dilute proteins. The ND Protein Precipitation Kit allows collection of proteins that would be missed by other methods.
Ideal for both routine and difficult work, the ND Protein Precipitation Kit stands alone among all methods. It offers the best combination of mildness, simplicity and effectiveness in protein precipitation.
High Yield Recovery
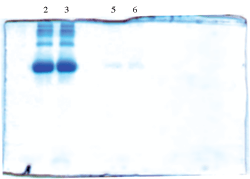
10ug BSA in 1ml vol and 50 ng of BSA in 200ul were prepared from stock and precipitated following kit instructions. 10ug and 50ng of BSA in 5 ul were prepared as controls. After running on a 12% gel, lanes 2 and 3 show control and recovered 10ug BSA. Lanes 5 and 6 show control and recovered 50ng BSA. Densitometry of 10ug BSA showed 91.9% recovery
Simplicity of Method

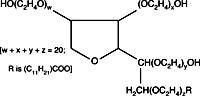
Reagent A and Reagent B form a coprecipitate with the protein.
After a simple wash, the protein pellet is ready to be redissolved in desired buffer.
Additional information
| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 8 × 3 × 10 in |
Protocol
Procedure:
- Add 1/20 volume Reagent A to sample in a centrifuge tube and mix well.
- Add 1/10 volume Reagent B to sample.
- Allow to precipitate for 20 minutes at room temperature. Precipitate is comprised of Reagent A:B complex along with trapped protein molecules.
- Collect precipitate by centrifugation and remove supernatant. The pellet will be large.
- Completely disperse pellet in acetone to dissolve away precipitated A:B complex. The solution should appear clear to cloudy, depending on protein concentration, with no visible clumps. Undispersed clumps will trap impurities which will be carried over into the final isolate.
- Collect proteins by centrifugation.
- To remove salts and surfactants, wash pellet with acetone, acetonitrile or 70% ethanol. This step may be repeated if desired for heavily contaminated samples, or for downstream applications requiring the highest purity proteins. Collect proteins by brief centrifugation if necessary.
- Redissolve pellet in desired buffer.
Safety Overview
Safety Summary (see SDS for complete information before using product):
Reagent A
Catalog Number: EC-888A
Appearance and Odor
Clear colorless aqueous Solution
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
May be harmful if swallowed. May cause severe eye irritation and possible injury. Causes skin and respiratory tract irritation.
Reagent B
Catalog Number: EC-888B
Safety Summary (see MSDS for complete information before using product):
Appearance and Odor
Aqueous Solution
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
WARNING! HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED OR INHALED. CAUSES IRRITATION TO SKIN, EYES AND RESPIRATORY TRACT.
Full SDS
ND Protein Precipitation Kit – Reagent A
View full SDS >
ND Protein Precipitation Kit – Reagent B
View full SDS >
- UV Shadowing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- Uneven Staining
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix-Buffer Strength
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Ohm’s Law
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
- The Electrophoresis Matrix
- The Agarose Matrix
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- SSCP Analysis
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
- Sample Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- PFGE and FIGE
- Peptide Mapping
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Multiphasic Buffer Systems
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Measuring Molecular Weight with SDS-PAGE
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- Isotachophoresis
- Isoelectric Focusing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Immuno-Electrophoresis / Immuno-Diffusion
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – Vertical Tube Gels
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Vertical Slab Gel System
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Horizontal Gel System
- Homogeneous Buffer Systems
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Guide Strip Technique
- Gel Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of RNA & Post Electrophoretic Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Electrophoresis Buffers-Choosing the Right Buffer
- Electrophoresis Buffers–The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Conformational Analysis
- Casting Gradient Gels
- Buffer Additives-Surfactants
- Buffer Additives-Reducing Agents
- Buffer Additives-Hydrogen Bonding Agents
- Blotches on Gel
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
- Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
- Activity Stains