Electrophoresis
Nuclistain
$107.00
Catalog Number: EC-730
- UV Free Visualization of DNA and RNA
- Improves Yield in PCR Purification from Agarose Gels
- Easy and Safe
Description
Catalog Number: EC-730
- UV Free Visualization of DNA and RNA
- Improves Yield in PCR Purification from Agarose Gels
- Easy and Safe
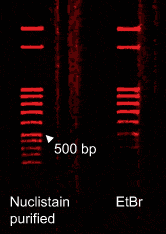
Nuclistain improves the yield of smaller and medium sized DNA (<500 bp) obtained by purification from agarose. One gel was stained with Nuclistain and the other with EtBr. The DNA was subsequently purified from each and then run side by side on a third gel, visualized by EtBr. The results show the improved yield from the Nuclistain.
Nuclistain is intended as a replacement for the conventionally used ethidium bromide for the rapid detection of double and single-stranded DNA and RNA in agarose and polyacrylamide gels. Its sensitivity is nearly comparable, with the capability of detecting as little as 10-50 ng of nucleic acid sample. The advantage of Nuclistain is that the results are visible under normal lighting conditions, eliminating the possibility of sample damage by UV radiation. Furthermore, Nuclistain visualization dramatically improves the yield of smaller and medium-sized DNA (<500 bp) obtained by purification from agarose. Nuclistain binding is reversible and does not modify nucleic acids.
Nuclistain is extremely easy to use. One 25 ml bottle of Nuclistain will make 2.5 liters of stain solution. The separated DNA appears as dark blue bands on a light blue background.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.3 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 6 × 3 × 3 in |
Protocol
Method of Use
- To prepare a working strength solution of Nuclistain, add one part Nuclistain concentrate to one-hundred parts of distilled water. Mix until the solution is uniform. Prepare sufficient stain solution to fully submerge the gel.
- Immerse the gel in the stain solution for 20–30 minutes.
- Immerse the gel in distilled water for 3–4 hours to destain the blue background. Bands can often be visualized minutes after destaining. However, for increased sensitivity, overnight destaining is recommended.
Safety Overview
Safety Summary (see SDS for complete information before using product):
Appearance and Odor
Opaque blue liquid.
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
MAY BE HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED.
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – CHRONIC HAZARD WARNING
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS HAVE SHOWN MUTAGENIC EFFECTS.
- UV Shadowing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- Uneven Staining
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix-Buffer Strength
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Ohm’s Law
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
- The Electrophoresis Matrix
- The Agarose Matrix
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- SSCP Analysis
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
- Sample Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- PFGE and FIGE
- Peptide Mapping
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Multiphasic Buffer Systems
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Measuring Molecular Weight with SDS-PAGE
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- Isotachophoresis
- Isoelectric Focusing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Immuno-Electrophoresis / Immuno-Diffusion
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – Vertical Tube Gels
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Vertical Slab Gel System
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Horizontal Gel System
- Homogeneous Buffer Systems
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Guide Strip Technique
- Gel Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of RNA & Post Electrophoretic Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Electrophoresis Buffers-Choosing the Right Buffer
- Electrophoresis Buffers–The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Conformational Analysis
- Casting Gradient Gels
- Buffer Additives-Surfactants
- Buffer Additives-Reducing Agents
- Buffer Additives-Hydrogen Bonding Agents
- Blotches on Gel
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
- Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
- Activity Stains