Electrophoresis
ProtoBlot Rapid Western Blotting Buffer (10X)
$49.00
Size: 1 Liter
- Blot in half the time versus conventional electroblotting buffers
- Very high-efficiency transfer
- Optimal pH; less harsh on proteins
Description
Size: 1 Liter
- Blot in half the time versus conventional electroblotting buffers
- Very high-efficiency transfer
- Optimal pH; less harsh on proteins
ProtoBlot Rapid Western Blotting Buffer is a relatively low conductivity buffer designed to replace tris/glycine (Towbin) buffer in wet (tank) transfer applications. It allows protein transfer from gels to nitrocellulose or PVDF at relatively higher voltages.
The speed of transfer of a protein from the gel to the membrane during a western blot is proportional to the electric field strength. It is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the distance between the electrodes and is expressed in V/cm. The amount of heat produced during the transfer is a function of the current flowing through the system. A lower conductivity buffer like ProtoBlot can be run at a higher voltage producing less heat because the current conducted will be lower. This allows for a shorter run time and more efficient transfer.
Key notes:
- For use the 10X buffer is diluted to 1X and ethanol or methanol is added to 10%-20%.
- The pH of the buffer at a 1X dilution is 8.4–8.5 which is the ideal pH for maximum transfer of most proteins.
- The transfer can be done with or without an ice pack or cooling system.
- Optimum transfer times will vary and have to be determined empirically, but a suggested starting point is 300V for 20 minutes.
Additional information
| Weight | 4.6 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 7 × 7 × 14 in |
Safety Overview
Safety Summary (see SDS for complete information before using product):
Appearance and odor
Odorless, colorless solution.
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
None
- UV Shadowing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- Uneven Staining
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix-Buffer Strength
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Ohm’s Law
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
- The Electrophoresis Matrix
- The Agarose Matrix
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- SSCP Analysis
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
- Sample Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- PFGE and FIGE
- Peptide Mapping
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Multiphasic Buffer Systems
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Measuring Molecular Weight with SDS-PAGE
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- Isotachophoresis
- Isoelectric Focusing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Immuno-Electrophoresis / Immuno-Diffusion
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – Vertical Tube Gels
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Vertical Slab Gel System
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Horizontal Gel System
- Homogeneous Buffer Systems
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Guide Strip Technique
- Gel Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of RNA & Post Electrophoretic Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Electrophoresis Buffers-Choosing the Right Buffer
- Electrophoresis Buffers–The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Conformational Analysis
- Casting Gradient Gels
- Buffer Additives-Surfactants
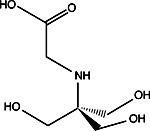
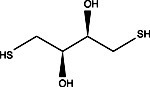
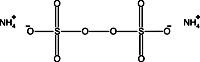
- Buffer Additives-Reducing Agents
- Buffer Additives-Hydrogen Bonding Agents
- Blotches on Gel
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
- Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
- Activity Stains