Electrophoresis
ProtoStain Blue
$112.00
Size: 1 liter
Get a free sample of ProtoStain Blue! Call us at (800) 526-3867 for details!
- The faster, more sensitive colloidal Coomassie Blue stain
- Bands appear in 15 minutes
- Safe, non-hazardous formula
Description
Size: 1 liter
- The faster, more sensitive colloidal Coomassie Blue stain
- Bands appear in 15 minutes
- Safe, non-hazardous formula
Get a free sample of ProtoStain Blue! Call us at (800) 526-3867 for details!
ProtoStain Blue is a colloidal Coomassie Blue G-250 solution that is a safer, more sensitive method for detecting proteins on electrophoresis gels. Bands begin to appear in only 15 minutes, and ProtoStain Blue has the ability to detect down to 1ng denatured BSA.
ProtoStain Blue is safe and nonhazardous, containing no methanol, acetic acid or phosphoric acid. Where local regulations permit, ProtoStain Blue can be poured down the drain, as it is not classified as a hazardous waste according to United States Title 40 Code of Federations (40 CFR 261.24 (a)) and EEC Directive 79/831/EEC Annex VII, JIS K 3363-1967 (always consult local and state regulations before disposing of any laboratory reagents).
Additional information
| Weight | 4.6 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 7 × 7 × 14 in |
Protocol
Method of Use
- Wash gel 3 times at 10 minutes each with deionized water on an orbital shaker. Decant wash solution. Longer washes give better consistency.
- After the last wash, add enough ProtoStain Blue solution to completely cover the gel. Invert bottle before use to resuspend particles before dispensing stain solution.
- Bands containing more than 1μg of protein will be detected within 15 minutes. For full sensitivity incubate the gel in the stain for at least 4-5 hours. Longer incubations in the stain will not adversely affect the gel or the staining sensitivity.
- Remove the stain and wash the gel in deionized water. Incubating the gel in water increases the sensitivity of detection by reducing the background to crystal clear. The gel is stable in water for up to a week without loss of sensitivity. There is no need to store the gel in a salt solution.
Safety Overview
Safety Summary (see SDS for complete information before using product):
Appearance and odor
Odorless, colorless solution.
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
None
- UV Shadowing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- Uneven Staining
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix-Buffer Strength
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Ohm’s Law
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
- The Electrophoresis Matrix
- The Agarose Matrix
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- SSCP Analysis
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
- Sample Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- PFGE and FIGE
- Peptide Mapping
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Multiphasic Buffer Systems
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Measuring Molecular Weight with SDS-PAGE
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- Isotachophoresis
- Isoelectric Focusing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Immuno-Electrophoresis / Immuno-Diffusion
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – Vertical Tube Gels
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Vertical Slab Gel System
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Horizontal Gel System
- Homogeneous Buffer Systems
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Guide Strip Technique
- Gel Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of RNA & Post Electrophoretic Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Electrophoresis Buffers-Choosing the Right Buffer
- Electrophoresis Buffers–The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Conformational Analysis
- Casting Gradient Gels
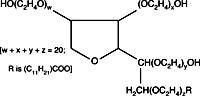
- Buffer Additives-Surfactants
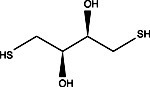
- Buffer Additives-Reducing Agents
- Buffer Additives-Hydrogen Bonding Agents
- Blotches on Gel
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
- Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
- Activity Stains