Electrophoresis
SequaGel UreaGel 29:1 Denaturing Gel System
$136.00 – $221.00
- Casts 29:1 denaturing gels for RNA or DNA analysis
- Easily cast up to 20% gels
- Certified nuclease-free
- Consistently crystal clear gels
Description
- Casts 29:1 denaturing gels for RNA or DNA analysis
- Easily cast up to 20% gels
- Certified nuclease-free
- Consistently crystal clear gels
Additional information
| Weight | 5 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 14 × 7 × 18 in |
Protocol
Procedure
Mix UreaGel System Components
Determine how much UreaGel 29:1 Concentrate, Diluent, and Buffer you need to make your gels using the formulas below. Combine the necessary components in an Erlenmeyer flask. Swirl gently to mix.
For 100 ml Gel Casting Solution:
Vc = (Vt) (X)/25
Vb = 0.1 (Vt)
Vd = Vt – (Vc + Vb)
where:
Vc = UreaGel 29:1 Concentrate Volume
Vb = UreaGel Buffer Volume
Vd = UreaGel Diluent Volume
Vt = Total Casting Solution Volume
X = % Gel Desired
EXAMPLE:
To make 100ml of an 8% gel, calculate the UreaGel solution volume to be added as follows:
Vc =(100) (8)/25 = 32ml UreaGel 29:1 Concentrate
Vb = 0.1 (100) = 10ml UreaGel Buffer
Vd = 100 – (32 + 10) = 58ml UreaGel Diluent
Add Initiators and Cast Gel
Add 40 microliters of TEMED for every 100 ml of gel casting solution. Swirl gently to mix. Add 0.8 ml of FRESHLY PREPARED 10% ammonium persulfate for every 100ml of gel casting solution. Swirl gently to mix. Cast the gel. Insert the comb and allow to polymerize one to two hours.
Safety Overview
Safety Summary (see MSDS for complete information before using product):
UreaGel 29:1 Concentrate
Appearance and Odor:
Clear colorless solution
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
WARNING! ACRYLAMIDE IS A NEUROTOXIN. HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED. sYMPTOMS OF EXPOSURE MAY INCLUDE NUMBNESS, TINGLING, SWEATING AND LOSS OF COORDINATION. MAY CAUSE ALLERGIC SKIN REACTION. MAY CAUSE EYE IRRITATION. POLYMERIZATION MAY OCCUR FROM EXCESSIVE HEAT OR CONTAMINATION.
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – CHRONIC HAZARD WARNING
CHRONIC TOXICITY HAZARD. ACRYLAMIDE MAY CAUSE NERVOUS SYSTEM DAMAGE. ACRYLAMIDE CAUSED CANCER AND MALE REPRODUCTIVE DISORDERS IN LABORATORY ANIMAL TESTS. RISK DEPENDS ON DURATION AND LEVEL OF EXPOSURE.
UreaGel Buffer
Appearance and Odor
Clear colorless solution
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
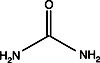
Urea
CAUSES IRRITATION TO SKIN, EYES, AND RESPIRATORY TRACT. UREA IS HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED OR INHALED.
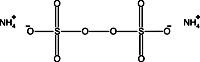
Boric Acid
CAUSES IRRITATION TO SKIN, EYES AND RESPIRATORY TRACT. BORIC ACID IS HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED OR INHALED.
Tris-Base
CAUSES IRRITATION TO SKIN, EYES, AND RESPIRATORY TRACT. HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED OR INHALED.
UreaGel Diluent
Appearance and Odor:
Clear, colorless solution
EMERGENCY OVERVIEW – IMMEDIATE HAZARD
CAUSES IRRITATION TO SKIN, EYES, AND RESPIRATORY TRACT. UREA IS HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED OR INHALED.
Full SDS
UreaGel 29:1 Concentrate
View full SDS >
UreaGel Diluent
View full SDS >
UreaGel Buffer
View full SDS >
- UV Shadowing
- Using PAGE to Determine Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight
- Uneven Staining
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix-Buffer Strength
- The Polyacrylamide Matrix
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis — Electrophoresis System Dynamics
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Ohm’s Law
- The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel Electrophoresis – Intro and Sample Mobility
- The Electrophoresis Matrix
- The Agarose Matrix
- Staining Proteins Immobilized on Membranes
- Staining Protein Gels with Coomassie Blue
- SSCP Analysis
- Southern Blotting
- Smeared Bands
- Silver Staining Protein Gels
- Silver Staining DNA Gels
- Sanger Sequencing
- Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
- Sample Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Sample Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
- S1 Mapping
- Run Conditions in Denaturing PAGE
- RNA Mapping
- RNA Electrophoresis
- Ribonuclease Protection
- Restriction Digest Mapping
- Radioactive Emissions and the Use of Isotopes in Research
- Protein Fixation on Gels
- Primer Extension
- Preparing Denaturing DNA & RNA Gels
- Preparation of Denaturing Agarose Gels
- Preparation of Agarose Gels
- Pouring Sequencing Gels
- Post-Electrophoretic Visualization with Nuclistain
- PFGE and FIGE
- Peptide Mapping
- PCR Analysis: Yield and Kinetics
- PCR Analysis: An Examination
- Overview of Western Blotting
- Northern Blotting
- Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Native PAGE of DNA
- Multiphasic Buffer Systems
- Mobility Shift Assay
- Methylation & Uracil Interference Assays
- Method for Western Blotting
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Mechanism of Immunostaining
- Measuring Molecular Weight with SDS-PAGE
- Maxam & Gilbert Sequencing
- Manual Sequencing
- Isotachophoresis
- Isoelectric Focusing
- In Gel Enzyme Reactions
- Immunostaining with Alkaline Phosphatase
- Immuno-Electrophoresis / Immuno-Diffusion
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – Vertical Tube Gels
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Vertical Slab Gel System
- Horizontal and Vertical Gel Systems – The Horizontal Gel System
- Homogeneous Buffer Systems
- Heteroduplex Analysis
- Guide Strip Technique
- Gel Preparation for Native Protein Electrophoresis
- Gel Preparation for Native PAGE of DNA
- Gel Electrophoresis of RNA & Post Electrophoretic Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis of PCR Products
- Faint bands, low background
- Faint Bands, High Background
- Ethidium Bromide Staining
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Electrophoresis Buffers-Choosing the Right Buffer
- Electrophoresis Buffers–The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- DNase I Footprinting
- DNA/RNA Purification from PAGE Gels
- DNA/RNA Purification from Agarose Gels – Electroelution
- Differential Display
- Denaturing Protein Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of DNA & RNA
- Coomassie Blue Stain- Troubleshooting
- Conformational Analysis
- Casting Gradient Gels
- Buffer Additives-Surfactants
- Buffer Additives-Reducing Agents
- Buffer Additives-Hydrogen Bonding Agents
- Blotches on Gel
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
- Biological Macromolecules – Proteins
- Autoradiography
- Autoradiographic Enhancement with Autofluor
- Automated Sequencers
- Analysis of DNA/Protein Interactions
- An Overview of Northern and Southern Blotting
- Alkaline Blotting
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – Uses and Variations
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA and RNA – An Introduction
- Activity Stains